
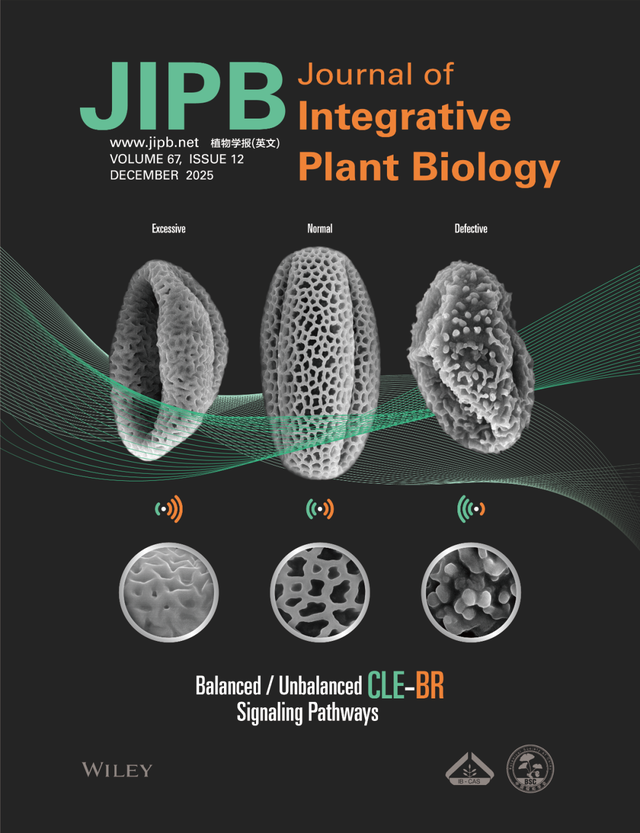
In nature, balance sustains life. Zhang et al. (pages 3216–3230) reveal how the small peptide CLE19 (in green color) and the brassinosteroid (BR, in orange color) hormone act as opposing forces to maintain balance in pollen wall formation in Arabidopsis. In this system, CLE19 signaling restrains BR output through the BSL–BIN2–BES1 cascade. When this equilibrium is disturbed, for example by too little BR or too much CLE19, the pollen wall becomes defective. Likewise, overly active BR signaling or insuffi cient CLE19 results in abnormal wall thickening and sterility. This study highlights the vital equilibrium between peptide and hormone signaling required for reproductive success in plants.
内容导览
一、Commentary
1.Introducing a win–win strategy for both rice yield and sheath blight resistance| 双赢突破——水稻抗纹枯病基因SBRR1被发现, AI育种助力抗病高产兼得
2.Divergent selection in moisture-responsive root-branching pathways between tropical and temperate maize germplasm
3.From uncontrolled to controllable: A novel approachfor nucleotidebinding, leucine-rich repeat bioengineering | 中国农业大学张永亮课题组发表植物NLR蛋白工程化改造评述文章
4.GI as a dynamic integrator: Synchronizing photoperiod and temperature signals to control flowering time in Arabidopsis
5.Native genetic switch enhances heat resilience, grain quality, and yield in rice | 中国科学家发现水稻“天然耐热开关”,高温下增产超九成且米质更优
二、Brief Communications
Overexpression of modified Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cyt2Aa in wheat strongly enhances aphid resistance | 青岛农业大学和山东省农业科学院作物所联合开发提高小麦蚜虫抗性的新策略
三、Abiotic Stress Responses
ZmSnRK2.10-mediated phosphorylation of ZmDNL1 attenuates ZmYAB15 activity to enhance drought resilience in maize | 中国农业大学巩志忠团队发现ZmSnRK2.10通过磷酸化ZmDNL1减弱ZmYAB15的转录活性以增强玉米抗旱性
四、Metabolism and Biochemistry
Metabolome study of rice population and resistance to brown planthopper | 武汉大学生命科学学院杂交水稻全国重点实验室何光存团队提出基于代谢标志物的水稻褐飞虱抗性预测模型并解析遗传调控新机制
五、Molecular Physiology
1.UBA2A regulates seed dormancy and the stability of chromatin-retained DOG1 messenger RNA
2.NUDIX hydrolases target specifi cinositol pyrophosphates and regulate phosphate homeostasis and bacterial pathogen susceptibility in Arabidopsis
六、Photosynthesis and Crop Physiology
Assembly mechanism of PSII-LHCII array from higher plants | 河南大学张立新、南方科技大学/清华大学隋森芳与华中农业大学高军团队合作阐明高等植物PSII-LHCII阵列组装机制
七、Plant Biotic Interactions
1.CPOP1 is a key enzyme required for nodule microenvironment control and successful symbiotic nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus | 中国科学院杨维才院士团队揭示宿主血红素合成酶CPOP1通过调控根瘤氧浓度实现豆科植物高效共生固氮
2.A multifunctional citrus-derived antimicrobial peptide controls vascular bacterial pathogens
3.Global profiling of lysinemalonylated proteins in rice elucidates the immune-regulatory mechanisms of malonylation under herbivore or viral stresses | 江苏省农业科学院方继朝-纪锐团队与扬州大学贺振团队合作揭示水稻赖氨酸丙二酰化修饰调控生物胁迫抗性机制
八、Plant Biotic Interactions
CLE19 suppresses brassinosteroid signaling output via the BSL-BIN2 module to maintain BES1 activity and pollen exine patterning inArabidopsis | 复旦大学常芳团队揭示CLE19小肽与BR激素拮抗调控花粉发育稳态的分子机制
01—Commentary
Introducing a win–win strategy for both rice yield and sheath blight resistance
Wenlong Guo, Qian Qian and Xiaoming Zheng
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70033

This commentary on Feng et al. (2025, Nat. Genet) discusses the role of SBRR1-R in sheath blight resistance, along with its importance for resistance gene mining in germplasm resources and the potential of molecular design breeding to enhance sheath blight resistance.
Divergent selection in moisture-responsive root-branching pathways between tropical and temperate maize germplasm
Sunil S. Gangurde, Chenglai Wu, Jiwang Zhang, BM Prasanna and Xuecai Zhang
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70065

This commentary on Scharwies et al. (2025, Science) discusses maize root branching in response to moisture gradients and highlights research gaps in investigation of the role of soil type and soil properties in driving weak or strong root hydropatterning in maize.
From uncontrolled to controllable: A novel approachfor nucleotidebinding, leucine-rich repeat bioengineering
Yi Li, Chenhao Ma, Xinchen Wang, Chenchen Zhong, Savithramma P. Dinesh-Kumar and Yongliang Zhang
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70046
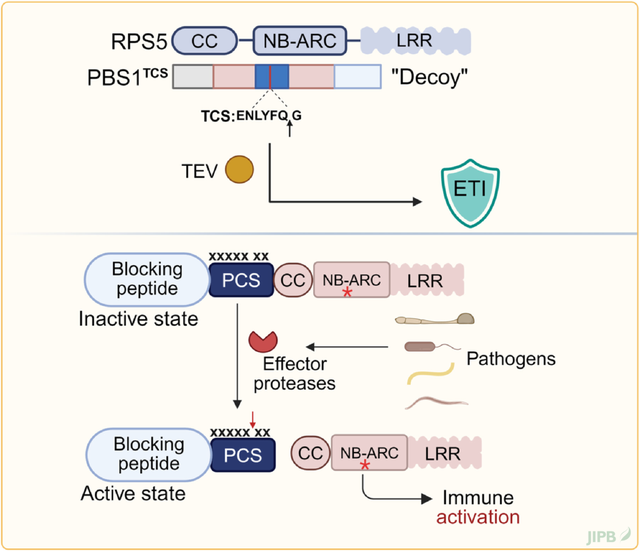
Gene scarcity and resistance breakdown limit the utility of plant NLRs. Findings in Nature by Wang et al. (2025) describe a bioengineering strategy using N-terminal blocking peptides to achieve tunable NLR activation, providing durable, broad-spectrum resistance to potyviruses in plants.
GI as a dynamic integrator: Synchronizing photoperiod and temperature signals to control flowering time in Arabidopsis
Gyeongik Ahn, Song Yi Jeong and Woe-Yeon Kim
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70051
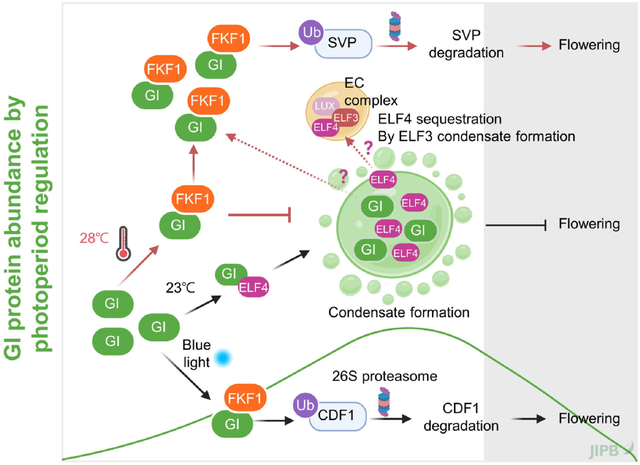
GIGANTEA (GI) integrates photoperiod and temperature signals to regulate flowering. Under high temperatures, suppression of GI liquid–liquid phase separation promotes flowering. This illustrates how plants coordinate photoperiodic and thermosensory cues to fine-tune development. GI also links stress responses and circadian control, highlighting its central role in environmental signal integration.
Native genetic switch enhances heat resilience, grain quality, and yield in rice
Muhammad Ali, Xiaohui Ma, Izhar Ali and Shuai Hu
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70043

This commentary describes a study showing that the natural thermo-responsive gene switch QT12 regulates rice thermotolerance by modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and storage protein synthesis. Dual transcriptional controls optimize grain quality and yield under heat stress. Multi-site field trials validated QT12 s potential for breeding heat-resilient rice, advancing climate-smart agriculture.
02—Brief Communications
Overexpression of modified Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cyt2Aa in wheat strongly enhances aphid resistance
Dian Wang, Ziyu Cao, Wang Chen, Hengyu Yan, Yulian Li, Zining Sun, Yiguo Liu, Genying Li and Guang Qi
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70038

Overexpression of modifi ed Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)-derived toxin fused with gutbinding peptides strongly enhanced aphid resistance in wheat.
03—Abiotic Stress Responses
ZmSnRK2.10-mediated phosphorylation of ZmDNL1 attenuates ZmYAB15 activity to enhance drought resilience in maize
Aifang Ma, Yuanpeng Qi, Yuemei Zhang, Yu Wang, Xiaoying Hu, Jingrong Li, He Ma, Zhihui Sun, Shan Jiang, Zhenkai Feng, et al.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70036

In maize, the kinase ZmSnRK2.10 phosphorylates the regulator ZmDNL1, disrupting its enhancement of the drought-suppressing transcription factor ZmYAB15, thus minimizing water loss and improving survival during drought.
04—Metabolism and Biochemistry
Metabolome study of rice population and resistance to brown planthopper
Tianzhu Li, Qian Zhang, Meng Ye, Yichen Cheng, Jing Yang, Jing Wang, Binglin Xing, Wei Guan, Jiamei Li, Chunyu Liu, et al.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70035

Metabolomic analysis of germplasm revealed that resistant rice varieties exhibit greater metabolic divergence while maintaining metabolic stability under brown planthopper feeding. The development of highly accurate prediction models using metabolic biomarkers, combined with the identifi cation of genes regulating key metabolites, provides powerful tools for molecular breeding and sustainable pest control.
05—Molecular Physiology
UBA2A regulates seed dormancy and the stability of chromatin-retained DOG1 messenger RNA
Ce Wang, Lien Brzeźniak, Sebastian Sacharowski, Michal Krzyszton, Veena Halale Manjunath, Mateusz Jan Olechowski, Anna Kulik and Szymon Swiezewski
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70056
In Arabidopsis, expression of DELAY OF GERMINATION 1 (DOG1), a key regulator of seed dormancy, is regulated not only at the level of transcription but also post-transcriptionally, at the level of mRNA stability.
NUDIX hydrolases target specifi cinositol pyrophosphates and regulate phosphate homeostasis and bacterial pathogen susceptibility in Arabidopsis
Robin Schneider, Klea Lami, Isabel Prucker, Sara Christina Stolze, Annett Strauß, Julie Marie Schmidt, Simon M. Bartsch, Kevin Langenbach, Esther Lange, Kevin Ritter, et al.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70060
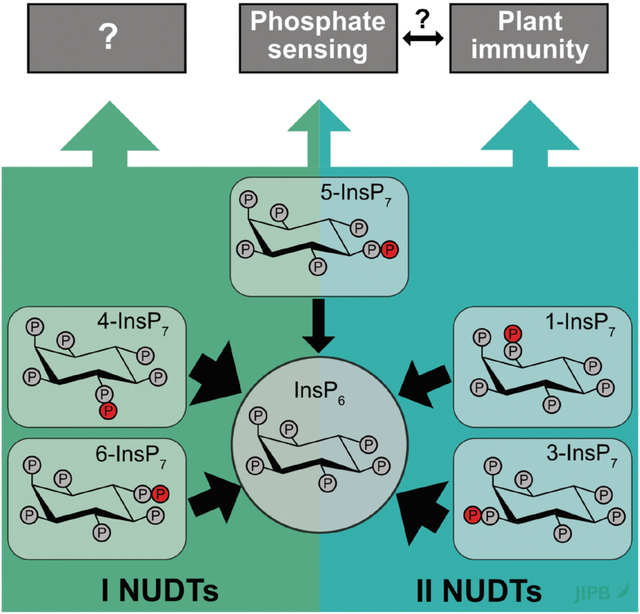
NUDIX-type hydrolase enzymes of subclade I and II preferentially target the inositol pyrophosphate messengers 4- and 3-InsP7, respectively. Inactivation of subclade II NUDTs disrupts phosphate homeostasis and enhances bacterial resistance, revealing connections between defense and nutrient signaling.
06—Photosynthesis and Crop Physiology
Assembly mechanism of PSII-LHCII array from higher plants
Jianghao Wu, Cang Wu, Shuaijiabin Chen, Chao Huang, Quan Wen, Weijun Lin, Chao Wang, Dexian Han, Dandan Lu, Xiumei Xu, et al.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70045

Plants efficiently harvest light by forming large, flexible arrays of key protein complexes in Photosystem II and the Light-harvesting Complex II. These structures enhance energy capture and protect against light damage, revealing a dynamic organizational principle crucial for plant photosynthesis and health.
07—Plant Biotic Interactions
CPOP1 is a key enzyme required for nodule microenvironment control and successful symbiotic nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus
Yu-Fang Tian, Yu Luo, Qi-Min Li, Zhi-Qin Zhang, Ya-Long Guo and Wei-Cai Yang
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70037
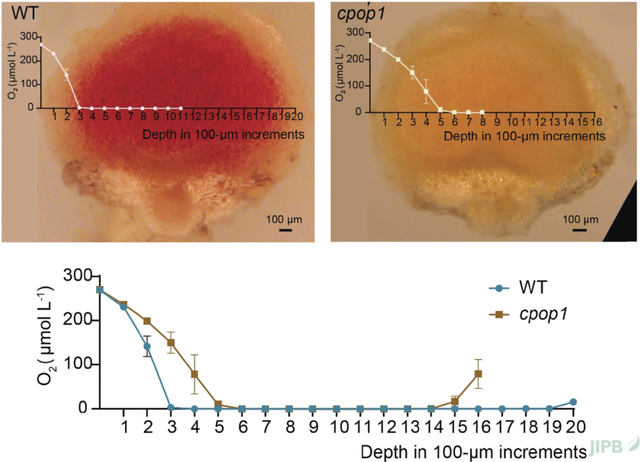
The enzyme coproporphyrinogen III oxidase plastid related 1 (CPOP1) creates a low-oxygen nodule environment for nitrogen fi xation within nodules of Lotus japonicus. CPOP1 makes heme, which helps control oxygen, and acts in infected cells; its knockout raises oxygen levels, suppresses nitrogen-fixing enzyme activity, and halts nitrogen fixation.
A multifunctional citrus-derived antimicrobial peptide controls vascular bacterial pathogens
Chien-Yu Huang, Marco Gebiola, Yali Wei, Kerry E. Mauck and Hailing Jin
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70057
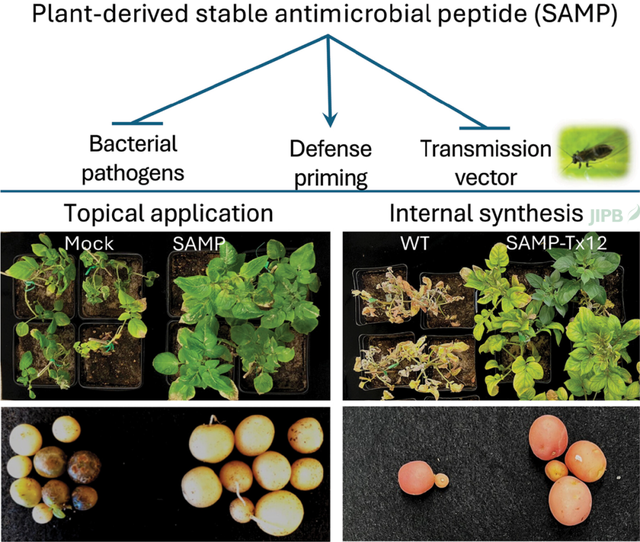
A plant-derived stable antimicrobial peptide (SAMP) from Australian fi nger lime (Citrus australasica) enhances potato resistance to Candidatus Liberibacter species. Potato and Arabidopsis plants producing SAMP synthesis showed increased resistance to vascular bacterial pathogens. This study provides evidence that SAMP can be used for crop bioengineering against various vascular pathogens.
Global profiling of lysinemalonylated proteins in rice elucidates the immune-regulatory mechanisms of malonylation under herbivore or viral stresses
Shuai Li, Xinyang Tan, Lei Yang, Xiaolong Deng, Miaomiao Li, Lang Qin, Liangxuan Qi, Jing Li, Guanghua Luo, Meng Yuan, et al.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70050
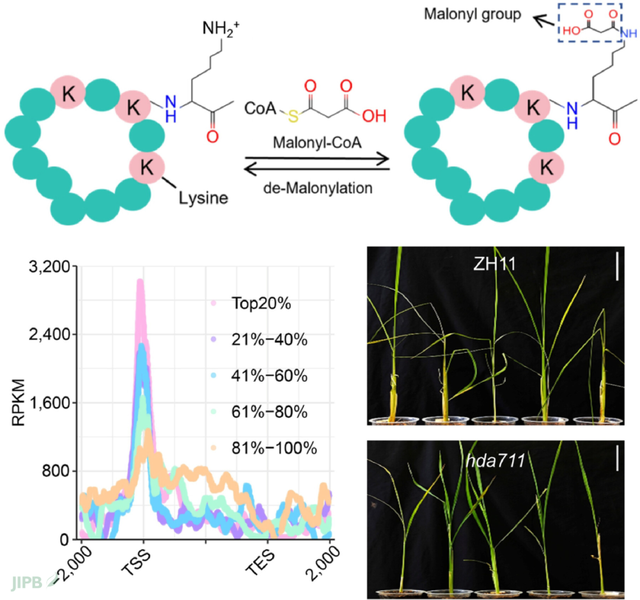
Lysine malonylation enhances rice resistance to herbivores/viruses via metabolic/chromatin modulation, with the histone deacetylase OsHDA711 as a negative regulator. OsHDA711 knockout boosts defense against brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens), striped stem borer (Chilo suppressalis), and rice stripe virus. These findings reveal epigenetic mechanisms for developing crops with broad-spectrum crop stress resistance.
08—Plant Reproductive Biology
CLE19 suppresses brassinosteroid signaling output via the BSL-BIN2 module to maintain BES1 activity and pollen exine patterning in Arabidopsis
Shuangshuang Wang, Shiting Zhang, Ying Yu, Jianzheng Wang, Jingya Wang, Mengyu Li, Jianan Lu, Juanying Ye, Hanji Li, Yeqiao Liu, et al.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70024
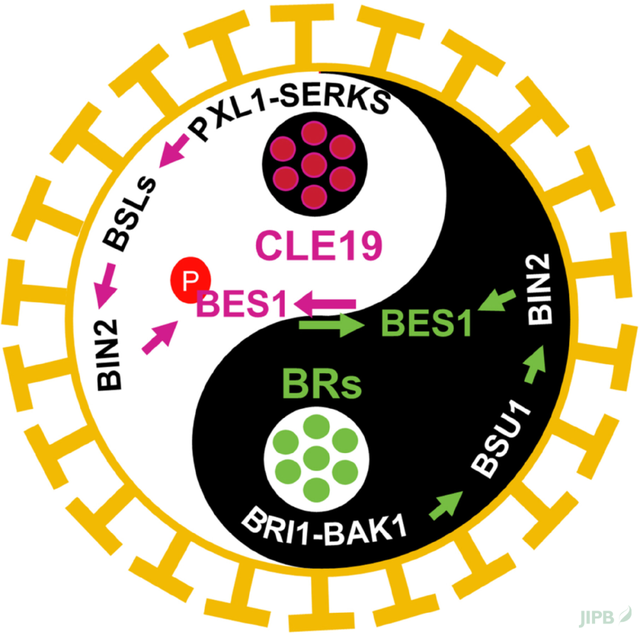
Antagonistic crosstalk between the microspore-derived CLE19 peptide and brassinosteroid signaling preserves pollen developmental homeostasis in Arabidopsis. CLE19 activates a protein phosphatase—kinase cascade to phosphorylate the transcription factor BES1, triggering its inactivation and suppressing brassinosteroid signaling outputs, thereby fi ne tuning male fertility under fluctuating conditions.